 C++ Tutorial – Getting Started An introductory tutorial for C++ programming language providing an overview of types, constants, operators, pointers, arrays and classes. Continue Reading
C++ Tutorial – Getting Started An introductory tutorial for C++ programming language providing an overview of types, constants, operators, pointers, arrays and classes. Continue Reading What is an Operating System? An operating system is a layer of software residing above hardware, hiding intricate details and providing an easy to use virtual machine. Continue Reading
What is an Operating System? An operating system is a layer of software residing above hardware, hiding intricate details and providing an easy to use virtual machine. Continue Reading String library functions in C The string library functions strlen, strcat, strcpy, strcmp, strstr, strtok can be used for string operations in C. Continue Reading
String library functions in C The string library functions strlen, strcat, strcpy, strcmp, strstr, strtok can be used for string operations in C. Continue Reading Strings in C A string can be either variable or constant. A variable string can be modified in the program whereas a constant string cannot be changed. Continue Reading
Strings in C A string can be either variable or constant. A variable string can be modified in the program whereas a constant string cannot be changed. Continue Reading Program to find the day of the week for a given date The Gregorian calendar was adopted in 1582. A C Program to find the day of the week for a given date as per Gregorian calendar is explained. Continue Reading
Program to find the day of the week for a given date The Gregorian calendar was adopted in 1582. A C Program to find the day of the week for a given date as per Gregorian calendar is explained. Continue Reading Flex Tutorial flex, "fast lexical analyzer", is a software tool for scanning input file and breaking it into recognizable chunks of text, called tokens. Continue Reading
Flex Tutorial flex, "fast lexical analyzer", is a software tool for scanning input file and breaking it into recognizable chunks of text, called tokens. Continue Reading Process synchronization The problem of synchronizing multiple concurrent processes is explained and a solution is provided with an example program. Continue Reading
Process synchronization The problem of synchronizing multiple concurrent processes is explained and a solution is provided with an example program. Continue Reading Regular Expressions in C Regular expressions are used for searching strings in text files. Regular expressions are explained with usage in a C program. Continue Reading
Regular Expressions in C Regular expressions are used for searching strings in text files. Regular expressions are explained with usage in a C program. Continue Reading Dining philosophers problem The dining philosophers problem is about deadlock in concurrent systems. The dining philosophers problem is explained with example programs. Continue Reading
Dining philosophers problem The dining philosophers problem is about deadlock in concurrent systems. The dining philosophers problem is explained with example programs. Continue Reading Program to generate a random password in C Strong passwords are generated by using random characters. A C program is provided to generate random passwords. Continue Reading
Program to generate a random password in C Strong passwords are generated by using random characters. A C program is provided to generate random passwords. Continue Reading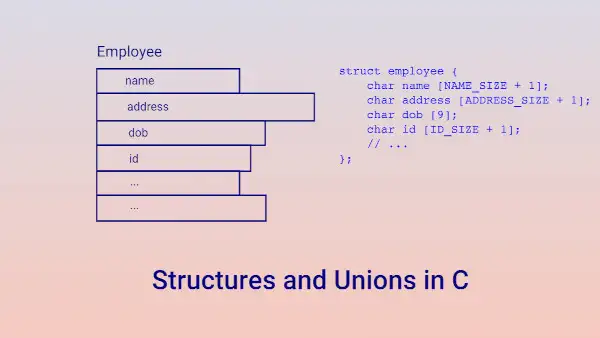 C Programming Tutorial 5: Structures and Unions A structure is a collection of variables, which are called its members. A union is a variable that holds different types at different times. Continue Reading
C Programming Tutorial 5: Structures and Unions A structure is a collection of variables, which are called its members. A union is a variable that holds different types at different times. Continue Reading C Programming Tutorial 4: Pointers and Arrays A pointer variable holds the address of another variable. An array stores the elements of the same type in consecutive locations. Continue Reading
C Programming Tutorial 4: Pointers and Arrays A pointer variable holds the address of another variable. An array stores the elements of the same type in consecutive locations. Continue Reading C Programming Tutorial 3: Control Flow Statements and Functions A C program comprises of functions. Functions comprise of statements, which determine the control flow in the program. Continue Reading
C Programming Tutorial 3: Control Flow Statements and Functions A C program comprises of functions. Functions comprise of statements, which determine the control flow in the program. Continue Reading C Programming Tutorial 2: Data Types and Expressions A C programming tutorial explaining data types, declarations, operators, conditional expressions and precedence and associativity rules. Continue Reading
C Programming Tutorial 2: Data Types and Expressions A C programming tutorial explaining data types, declarations, operators, conditional expressions and precedence and associativity rules. Continue Reading C Programming Tutorial 1 – Getting Started A C programming tutorial for beginners, explaining constants, variables, expressions, input and output and overall program structure. Continue Reading
C Programming Tutorial 1 – Getting Started A C programming tutorial for beginners, explaining constants, variables, expressions, input and output and overall program structure. Continue Reading